If you develop applications using the Laravel framework, you might notice that sometimes the AI assistants struggle to follow Laravel-specific conventions and best practices or can’t fetch the latest documentation. This will cause inaccuracies and inefficiencies in your development process, making it harder to maintain code quality and get the full power of Laravel’s new and elegant features.
Laravel Boost MCP Server was released by the core Laravel team to address these challenges. It is designed to integrate AI capabilities directly into your Laravel development workflow. By using Laravel Boost, developers can access to hadful of tools to bridge the gap between AI assistants and Laravel’s unique ecosystem.
Let’s create a new Laravel project and see how Laravel Boost can be installed and used,
Installing Laravel Boost #
You can install Laravel Boost via Composer. First, create a new Laravel project, navigate to the project directory, and then require the Laravel Boost package:
composer require laravel/boost --devMake sure to install Laravel Boost as a development dependency to avoid including it in your production builds. After installation, you have to run the following command to initialize Laravel Boost in your project:
php artisan boost:installIn the latest versions of Laravel Boost, package developers can integrate their package documentations into the Boost MCP server. This allows AI assistants to access up-to-date information about third-party packages. When I installed my new Laravel project, I have selected the Livewire option with default authentication scaffolding. So, in the first step I’m prompted to install the laravel/fortify documentation into the Boost MCP server. You can accept it or skip it if you don’t need it.
This command will detect what IDEs and AI assistants you are using and prompt you to confirm the installation. First you will be asked to choose your IDE:
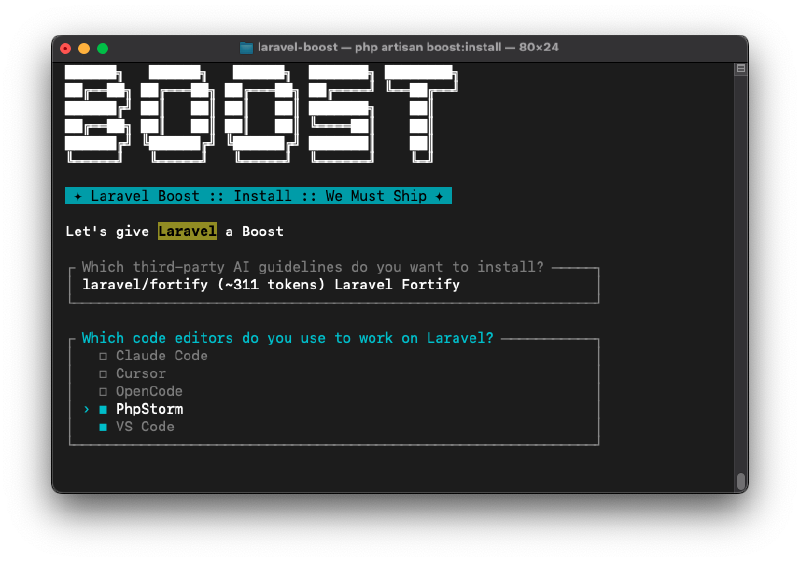
In my case, it’s PhpStorm and VSCode. After selecting the IDEs, you will be prompted to choose the AI assistants you want to integrate with Laravel Boost:
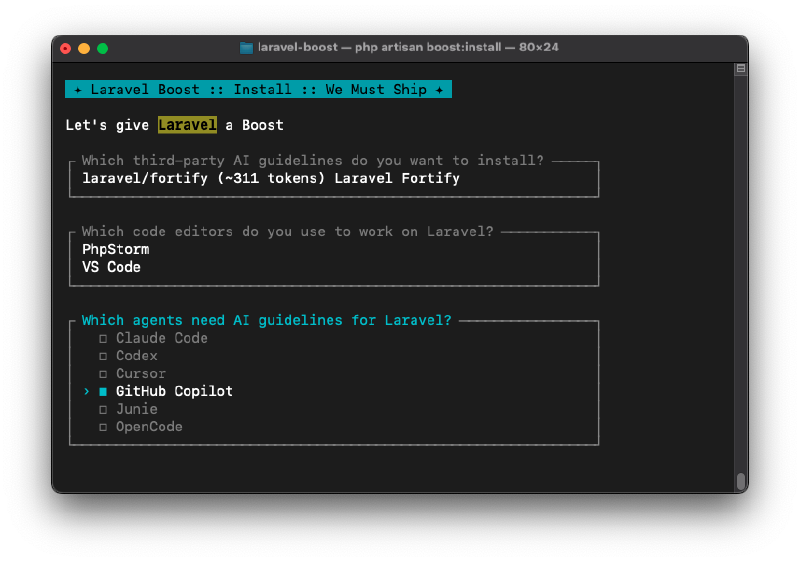
After selecting the AI assistants, Laravel Boost will configure the necessary settings for each IDE and AI assistant and set up the MCP server. The installation process will show you the list of packages that guidelines are installed.
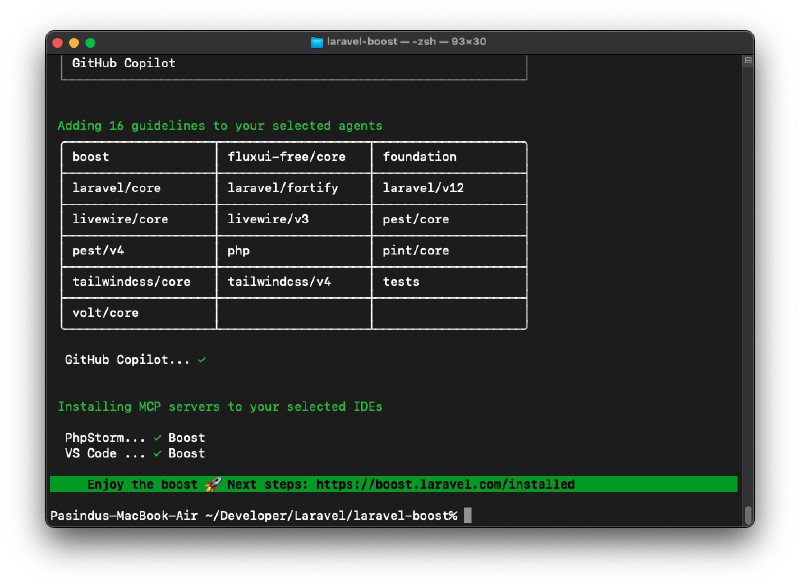
As you can see, Laravel Boost has successfully identified the installed packages like Livewire and FluxUI and added their guidelines to the respective directories, so selected AI assistants can access them. So in my case, I have selected GitHub Copilot as the AI assistant, so the guidelines are added to the .github/copilot-instructions.md file.
If you check the guideline files generated by Laravel Boost, you will see that they contain detailed information about the detected packages, including usage instructions, configuration options, and best practices. This will help AI assistants provide more accurate and context-aware suggestions when you are working with these packages. On top of Boost created guidelines, you can also add your own custom guidelines to further tailor the AI assistant’s behavior to your project’s specific needs.
If you have installed Laravel Boost correctly, the AI assistants will automatically start using the guidelines and tools provided by it when you are coding in your IDE or CLI.
Using Laravel Boost #
Laravel Boost provides bunch of useful MCP tools to give the AI assistants more relevant context about your Laravel project. Here are the full list of tools provided by Laravel Boost:
| Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| Application Info | Read PHP & Laravel versions, database engine, list of ecosystem packages with versions, and Eloquent models |
| Browser Logs | Read logs and errors from the browser |
| Database Connections | Inspect available database connections, including the default connection |
| Database Query | Execute a query against the database |
| Database Schema | Read the database schema |
| Get Absolute URL | Convert relative path URIs to absolute so agents generate valid URLs |
| Get Config | Get a value from the configuration files using “dot” notation |
| Last Error | Read the last error from the application’s log files |
| List Artisan Commands | Inspect the available Artisan commands |
| List Available Config Keys | Inspect the available configuration keys |
| List Available Env Vars | Inspect the available environment variable keys |
| List Routes | Inspect the application’s routes |
| Read Log Entries | Read the last N log entries |
| Report Feedback | Share Boost & Laravel AI feedback with the team, just say “give Boost feedback: x, y, and z” |
| Search Docs | Query the Laravel hosted documentation API service to retrieve documentation based on installed packages |
| Tinker | Execute arbitrary code within the context of the application |
As you can see, Laravel Boost provides a wide range of tools that allow AI assistants to interact with your Laravel application in a more meaningful way. For example, the “Last Error” tool allows AI assistants to read the last error from the application’s log files, which can help them diagnose issues and bugs more effectively. The “Search Docs” tool allows AI assistants to query the Laravel hosted documentation API service to retrieve relevant documentation based on the installed packages in your project. Let’s try some of these tools in a real project,
Get application info #
You can ask the AI assistant to provide you with information about your Laravel application. If you ask “list the packages and their versions installed in this application”, the AI assistant will use the “Application Info” tool to fetch the list of installed packages and their versions.
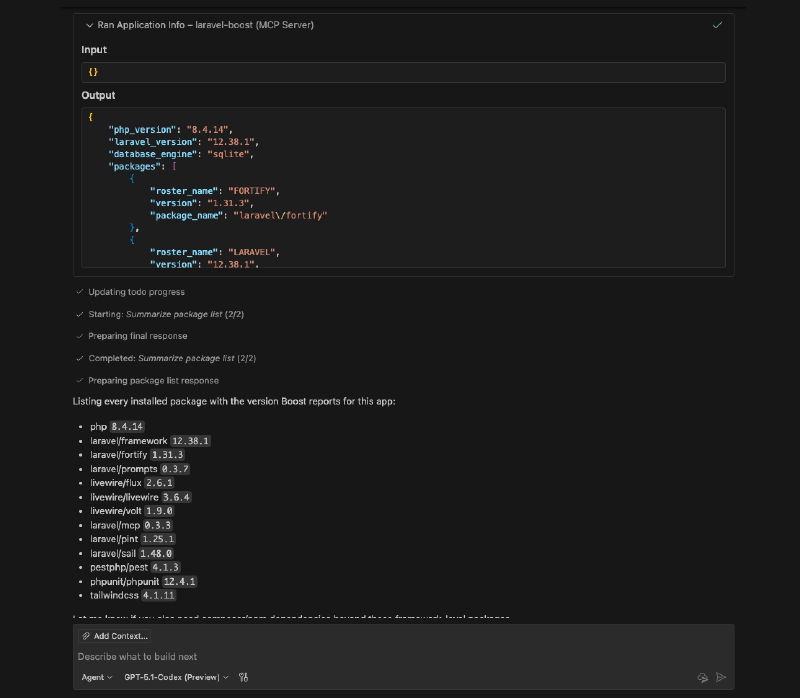
If you closely, the LLM has used the “Application Info” tool to get the list of installed packages and their versions, then the tool returned the information (context) to the LLM as a JSON object.
Documentation Search #
You can ask the AI assistant to search for specific documentation related to your Laravel project. For example, if you want to know how to get a difference between two dates using Carbon, you can ask “how to get the difference between two dates using Carbon in Laravel?”. The AI assistant will use the “Search Docs” tool to fetch relevant documentation from the Laravel hosted documentation API service. Then it will provide those new contexts back to AI agent to generate accurate code snippets.
Database Query #
This is my favorite tool in Laravel Boost. You can ask the AI assistant to execute a database query and return the results. You can run a query like “get the names and email addresses of all first 10 users in the users table”. The AI assistant will use the “Database Query” tool to execute the query and return the results.
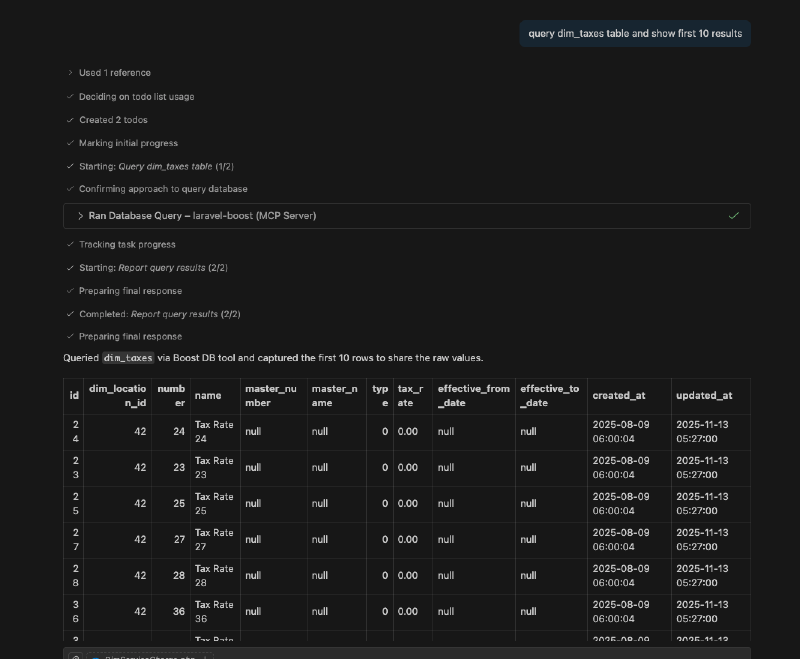
In above example, the LLM has used the “Database Query” tool to execute the SQL query and return the results as a JSON object. Let’s say you want to write a new migration for your database and you need to know the current schema of a table. The AI agent can use the “Database Schema” tool to fetch the schema right from your database and with correct context, it can generate the migration file for you. Another great use case of this tool is to write factory and seeders, You can ask the AI assistant to “create a factory and seeder for the users table based on its current schema”. The AI assistant will use the “Database Schema” tool to fetch the schema of the users table and then generate the factory and seeder code accordingly. You don’t need to provide any additional context about the table structure.
Provide Feedback #
Laravel Boost also allows you to provide feedback directly to the Laravel AI team. If you encounter any issues or have suggestions for improvement, you can simply say “give Boost feedback: [your feedback here]”. The AI assistant will use the “Report Feedback” tool to send your feedback to the Laravel AI team for review.
You can do some wild stuff with Laravel Boost MCP server, so I would suggest you to try it out in your Laravel project and explore the various tools and features it offers. Currently, Laravel Boost only supports for applicatio that use Laravel 10 and above. You can find more information about it on the Boost GitHub repository.