The field of artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving, with new models, technologies, and tools emerging regularly. One of the latest improvements in this space is the Model Context Protocol (MCP), which is designed to give AI agents a more structured way to interact with applications and external data sources. Claude AI’s creators, Anthropic, introduced MCP on November 25, 2024, and it has since gained significant attention in the AI community. This protocol enables secure, standardized connections between AI models and various applications, allowing AI agents to access databases, files, APIs, documentations, and more. This can be compared to how web applications use APIs to communicate with each other, or much like a universal adapter for electronic devices. Anthropic has made MCP open-source, allowing developers to implement it in their own applications and services. Recently released models like Claude 4.5, GPT-5 also has a great ability to use tool calls, which is done through MCP.
The Origins and Purpose of MCP #
MCP’s development stems from the limitations of early AI integrations. Before MCP, developers had to create broken and inefficient systems to build connectors for each AI model to interface with every data source or tool. Anthropic’s announcement positioned MCP as a solution to these challenges, breaking down information barriers and enabling AI agents to produce more relevant, context-aware responses. MCP draws inspiration from existing protocols like Language Server Protocol (LSP), which standardizes communication between code editors and language servers. MCP reuses message-flow concepts to standardize interactions.
The main purpose of MCP is to act as a middle man between AI models and external resources. Using MCP, LLMs can read files, query databases, handle prompt files, call APIs, and interact with other applications in a secure and standardized manner. Programmers can use AI agents better than before, as MCP can provide context and information that the AI model might not have been trained on or simply doesn’t know.
Architecture and Protocol Structure of MCP #
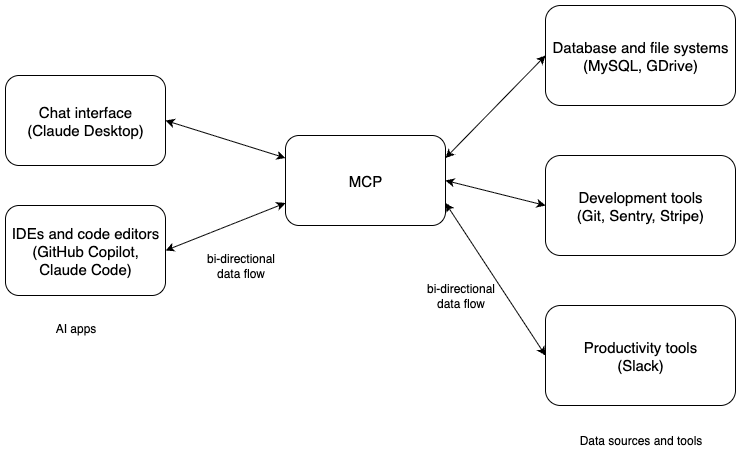
MCP operates on a client-server model. The MCP client is typically the AI application or LLM, such as Claude or GPT-5. The client initiates requests for data or actions. Then the MCP server exposes the outside resources, such as databases and tools, making them accessible to the client. Basically, the LLM calls the MCP server using its tool calling ability, and the MCP server handles the requests and responses back with new context to the LLM. LLM then can proceed with the new context. This communication happens over JSON-RPC 2.0, with support for stdio and HTTP transports. This bi-directional communication enables AI to not only get information but also send updates and trigger new actions.
This protocol structure is modular and extensible. Messages are formatted in JSON. MCP client can send a request to query a PostgreSQL database, and the server would authenticate, execute the query, and return results while applying data masking for security. MCP also supports contextual metadata tagging which allows AI to maintain state across interactions. This is crucial for complex tasks like multi-step coding or data analysis.
Developing a MCP server needs some SDKs available in different programming languages. For example, Anthropic provides many SDKs for different languages such as Python, JavaScript, PHP and more. You can find the list of SDKs here. This architecture allows developers to create custom MCP servers for their specific applications and proprietary data while ensuring compatibility and respecting permissions.
Key Features and Benefits of MCP #
MCP’s open source nature encourages community contributions and innovation. AI applications gain access to a vast ecosystem of tools and data sources, enhancing their capabilities. As an example think about a personalized assistant that pull data from your calendar, emails, and task manager to provide recommendations and reminders, or a desktop agent which we can delegate tasks and it can interact with your files, web browser, and other applications to complete tasks on your behalf. The real and grounded data makes AI agent responses more accurate and relevant with less hallucinations.
What is an MCP Server? #
The MCP server is the backbone of the Model Context Protocol. It serves as the intermediary that connects external systems to AI clients. It’s basically a specialized program that exposes resources like files, APIs, or databases to AI models. Programmers can build MCP servers to parse AI requests and deciding on actions such as querying backends. For example, a Stripe MCP server can get updated documentations from Stripe and expose them to a LLM, then a coding agent can use those context to implement a payment for a web application with higher accuracy.
Setup of MCP Servers #
Different AI applications and code editors setup MCP servers in different ways. Each editor also can have multiple ways of setting up MCP servers. In Visual Studio Code, you can set up an MCP server by installing an extension that supports MCP. Once the extension is installed, you can configure it to connect to your desired MCP server by providing the server’s URL and any necessary authentication details. After configuration, you can start using the MCP features within VS Code, allowing you to interact with external resources directly from your editor.
If you want to configure MCP servers for a specific project, you can add the server configuration to your workspace in the .vscode/mcp.json file. This allows you to share the same MCP server configuration with your project team. Then select the Add Server button in the editor to add a template for a new server. VS Code provides IntelliSense for the MCP server configuration file. The below example shows how to configure the GitHub remote MCP server.
{
"servers": {
"github-mcp": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.githubcopilot.com/mcp"
}
}
}
In the chat interface, you can select the configured MCP server and its tools to use. You can also configure multiple MCP servers and use them parallely, but be aware that higher number of MCP servers can confuse the LLM and lead to unexpected results.
This is a link to the official registry of VS Code MCP servers where you can find more MCP servers to use.
In a upcoming post, I will show you how to build your own MCP server from scratch using PHP and the MCP PHP SDK. Stay tuned!